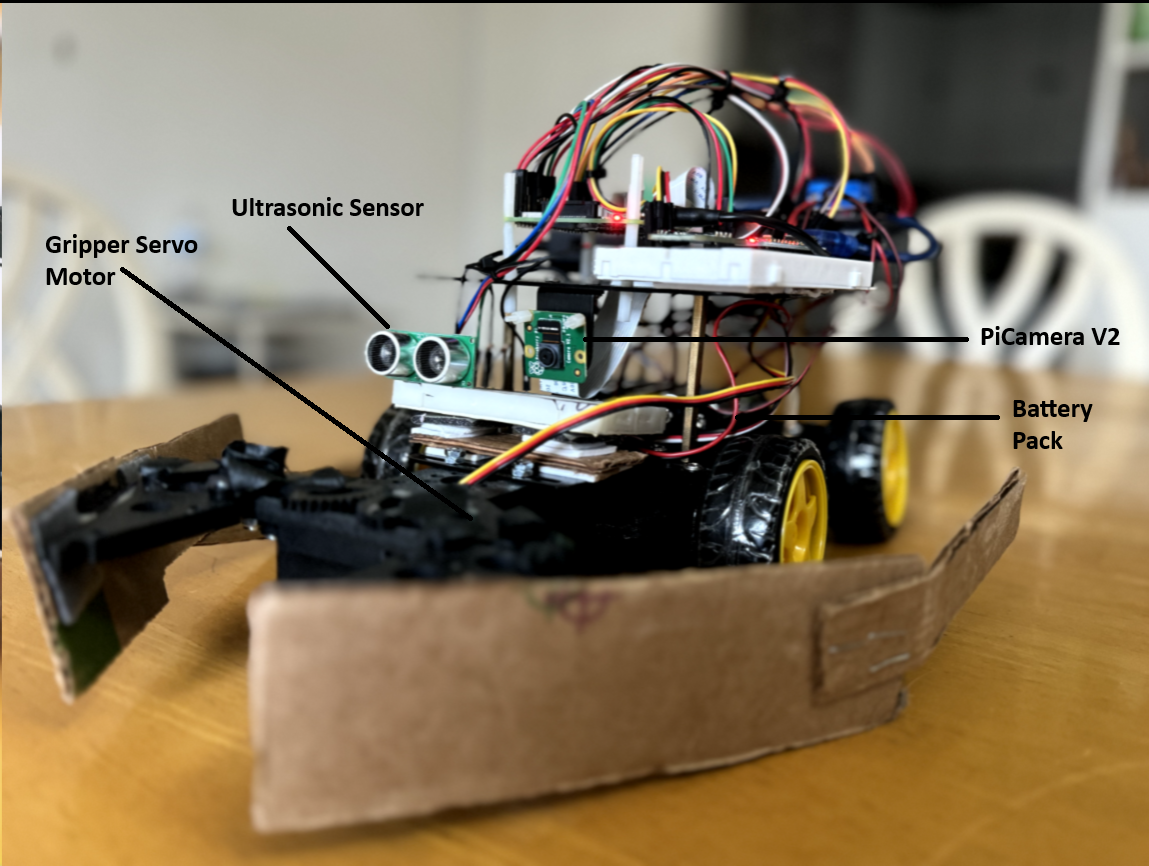
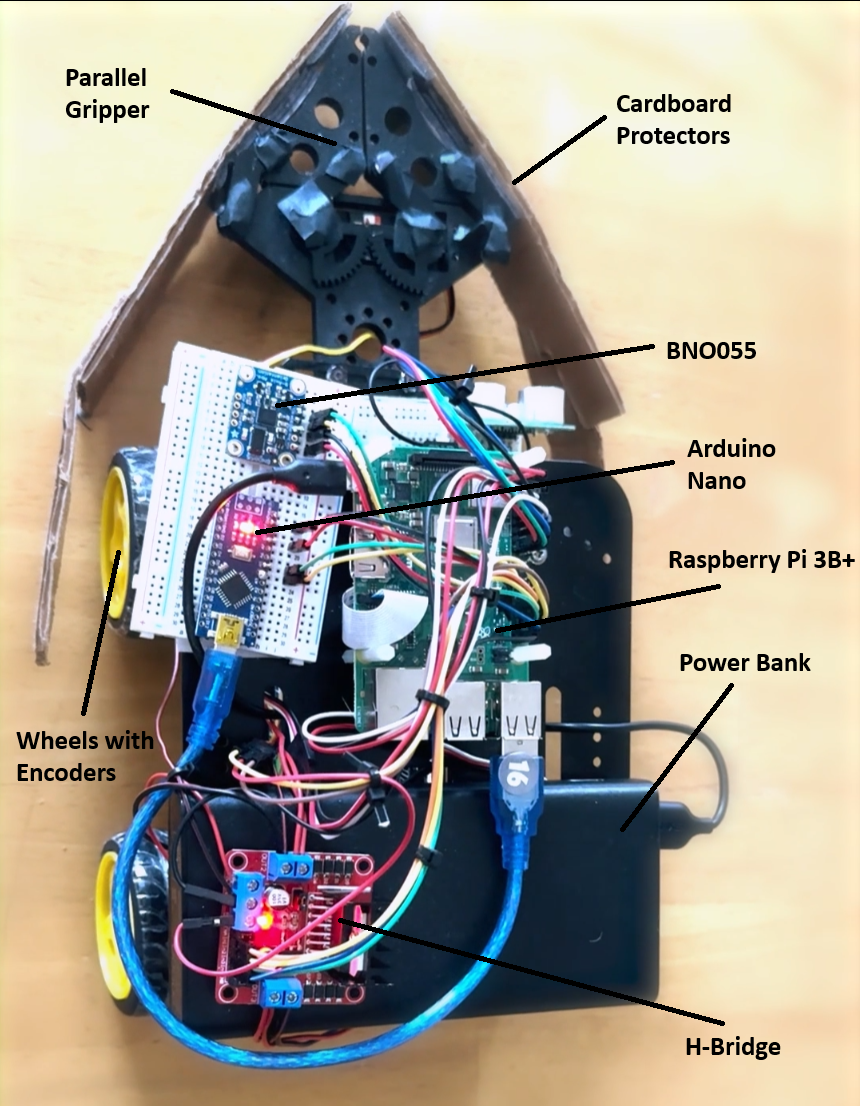
Project Overview
This project focuses on the design and implementation of an autonomous mobile manipulator robot capable of performing complex tasks in dynamic environments. The robot is engineered to navigate through industrial-like settings, detect and differentiate construction blocks, and transport them to designated locations, all while avoiding obstacles and optimizing task efficiency.
Features
- Integrated Design: Combines a mobile platform with a manipulator arm to handle both navigation and object manipulation.
- Autonomous Navigation: Uses landmark-based coordinates and sensor fusion for robust path planning and real-time obstacle avoidance.
- Advanced Object Interaction: Integrates vision-based detection (via OpenCV) and sonar sensors for accurate object recognition and interaction.
- Optimized Task Execution: Implements efficient task planning algorithms to reduce cycle times and improve overall performance.
Project Structure
Robot Construction
- Mobile Platform:
- Equipped with motors, wheels, and motor drivers for precise locomotion.
- Integrated with sonar sensors for distance measurement and obstacle detection.
- Manipulator Arm:
- Features a servo gripper assembly to handle objects securely.
- Designed for reliable pick-and-place operations in dynamic settings.
- Embedded System:
- Powered by a Raspberry Pi, which manages sensor data, vision processing, and control algorithms.
- Utilizes a camera for real-time object detection and environmental mapping.
Control Systems and Code Architecture
- Control Algorithms:
- Developed based on kinematic and dynamic models to ensure precise coordination between the mobile base and manipulator arm.
- Implements feedback loops using sensor data to adjust motion trajectories in real time.
- Code Overview:
- The primary control logic is contained in
test.py, which orchestrates sensor integration, image processing, and motor control. - Key Functions in
test.py:- Sensor Data Acquisition:
Retrieves inputs from sonar sensors and camera. This data is processed to detect obstacles and identify target objects. - Vision Processing:
Utilizes OpenCV for real-time image analysis to locate construction blocks. Algorithms filter and process frames to ensure reliable object recognition. - Motion Control:
Uses Python libraries such as RPi.GPIO to send commands to the motors based on the control algorithm’s output. - Path Planning:
Applies landmark-based navigation techniques and optimization routines from SciPy and NumPy to compute efficient paths and adjust robot trajectory dynamically.
- Sensor Data Acquisition:
- The primary control logic is contained in
Methodology
-
Hardware Integration:
The system integrates a mobile base, a manipulator arm, and multiple sensors (camera and sonar) into a unified platform. Emphasis was placed on ensuring reliable sensor calibration and seamless hardware-software integration. -
Control Algorithm Design:
Control algorithms were designed to blend kinematic modeling with real-time sensor feedback, enabling the robot to dynamically adjust its path and manipulation strategy. -
Path Planning & Task Optimization:
The robot uses a landmark-based navigation system to calculate efficient paths while dynamically avoiding obstacles. Optimization routines minimize task cycle time and improve operational accuracy. -
Object Detection & Interaction:
OpenCV is employed for image processing, which, combined with sonar data, allows the robot to accurately detect and interact with construction blocks under varying lighting and environmental conditions.
Key Challenges and Solutions
-
Part Recognition:
Overcame challenges in object recognition by fine-tuning image processing algorithms and integrating complementary sensor data. -
Sensor Calibration:
Implemented rigorous calibration routines for sonar sensors and the camera to ensure accurate and reliable measurements. -
Environmental Adaptation:
Developed robust control strategies to maintain performance in dynamic environments with fluctuating lighting and obstacles.
Performance Metrics
-
Task Success Rate:
Achieved a high success rate in locating and transporting construction blocks. -
Navigation Accuracy:
Maintained precise control with minimal deviation from planned trajectories. -
Cycle Time Reduction:
Optimized control algorithms led to a significant decrease in task cycle times. -
Obstacle Avoidance:
Demonstrated reliable real-time obstacle detection and avoidance in dynamic conditions.
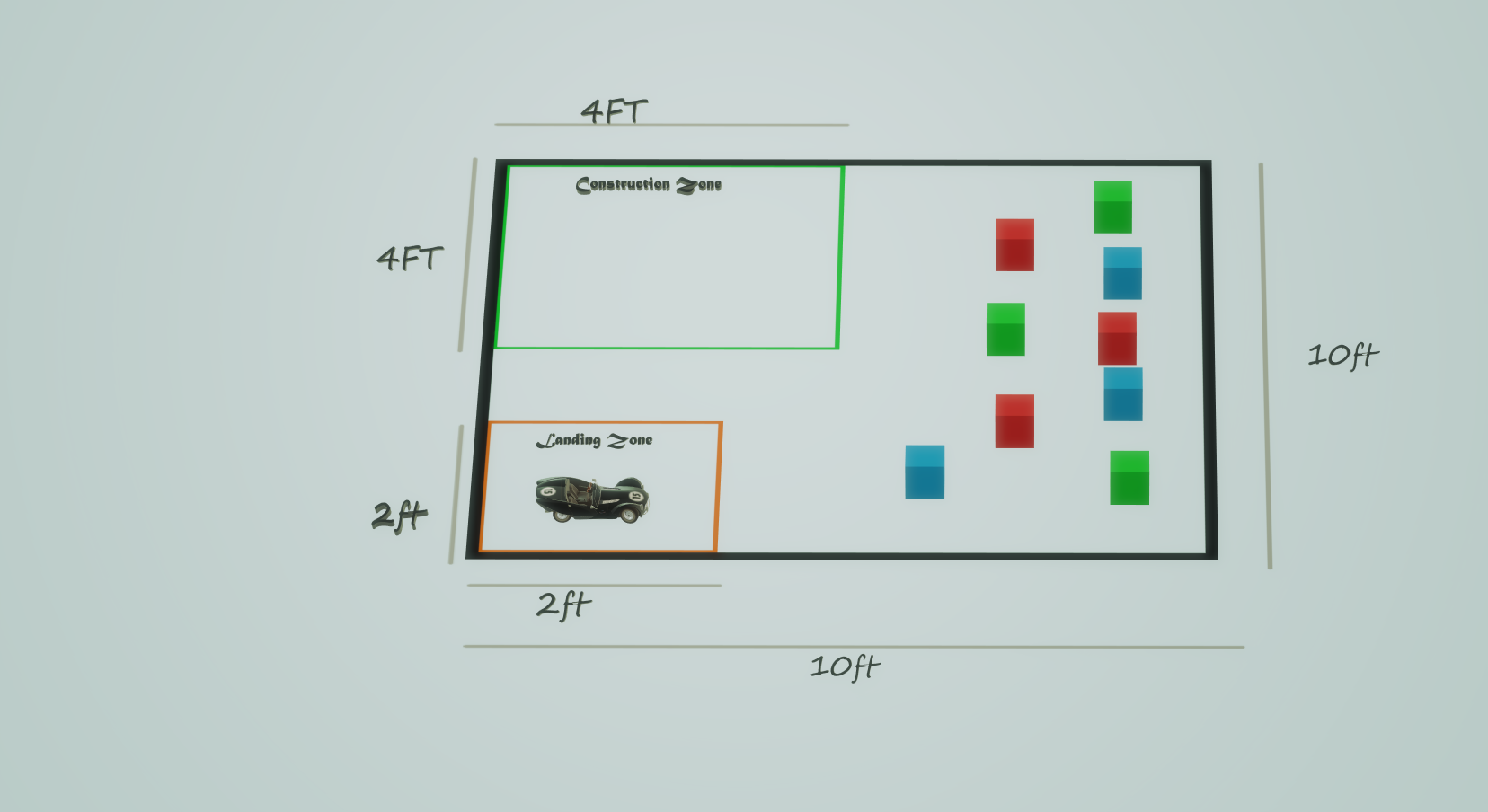
Visuals
Robot Model
Simulation Arena
Progress Video
Conclusion
This project successfully demonstrates an autonomous mobile manipulator robot capable of complex navigation and precise object handling. By integrating advanced sensor fusion, real-time control algorithms, and efficient path planning, the robot is able to operate reliably in dynamic environments. Future enhancements could include refined machine learning-based object recognition and expanded autonomous decision-making capabilities.